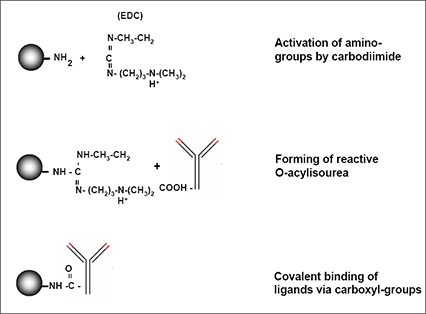
SiMAG - Amine by Carbodiimide Method
This procedure describes covalent coupling of carboxyl-group containing ligands such as antibodies, proteins or low molecular substances to SiMAG-Amine by the carbodiimide method.
The carbodiimide method is a binary covalent binding system and guarantees therefore a good reproducibility of the immobilization.
Carbodiimides react with the terminal amino-groups from the magnetic beads to highly reactive O-acylisourea derivatives and react readily with carboxyl-groups of the ligands.
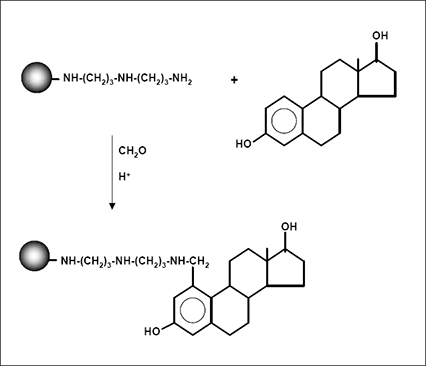
SiMAG - Amine by Mannich Condensation
This procedure describes the immobilization of compounds via aromatic ring to SiMAG-Amine by the Mannich reaction.
The Mannich reaction is useful for the coupling of compounds such as drugs, steriodal compounds, dyes, or other organic molecules which do not contain reactive components, e.g. primary amines, carboxylic acids, aldehydes or sulfhydryl groups.
The ligands are coupled by condensation with formaldehyde to terminal amino groups of the beads.
The coupling via Mannich reaction forms very stable covalent bonds which are useful for most affinity separations.